There are five different types of alcoholics: Young Adult Alcoholics, Functional Alcoholics, Intermediate Familial Alcoholic, Young Antisocial Alcoholics, and Chronic Severe Alcoholics. In this article, we’ll break down each type of alcoholic, their main traits, the risks they face, and the best ways to help them recover.
What Defines an Alcoholic?

First of all, what defines being an alcoholic? Being considered an alcoholic typically means that a person has a physical or psychological dependence on alcohol. This often includes:
- Continuing to drink despite negative consequences on health or life.
- Inability to control alcohol consumption.
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking.
- Prioritizing alcohol over responsibilities, relationships, or personal well-being.
- Needing to consume more alcohol to achieve the same effects (tolerance).
5 Types of Alcoholics
| Type | Profile |
|---|---|
| Young Adult Alcoholics | Typically in their early 20s, they often start drinking in social settings but gradually increase their consumption. |
| Functional Alcoholics | Maintains work, relationships, and a seemingly normal life despite excessive drinking. |
| Intermediate Familial Alcoholics | Typically has a family history of alcoholism and struggles with genetic predisposition. |
| Young Antisocial Alcoholics | Tends to begin drinking at a younger age and often has co-occurring antisocial behaviors or mental health issues. |
| Chronic Severe Alcoholics | Often middle-aged, drinking is frequent and intense, leading to serious health and social problems. |
Young Adult Alcoholics

Young adult alcoholics are one of the most common subtypes of alcoholism. They typically fall within the age range of 18 to 25 and often begin drinking in their late teens. Unlike other groups, they generally do not have mental health disorders or a family history of alcoholism, although environmental factors such as peer pressure and cultural influences heavily impact their drinking habits.
Support and Treatment
Young adult alcoholics are less likely to seek traditional treatment, often due to denial or a lack of perceived need. Peer-focused programs, counseling, and educational interventions about alcohol’s risks can be effective in addressing their habits early on.
Functional Alcoholics

Functional alcoholics are individuals who maintain outward stability in their personal and professional lives despite their problematic drinking habits. Despite battling alcoholism, they frequently succeed in their jobs, uphold wholesome relationships, and carry out their every day’s task. Because of their high-functioning lifestyle, which hides the underlying problem, this subtype is extremely hard to identify.
Support and Treatment
Functional alcoholics may resist seeking help because they perceive their drinking as manageable. Interventions that focus on long-term health risks and the potential for their drinking to spiral out of control are often effective. Treatment approaches can include counseling, peer support groups, and personalized therapy that addresses their unique challenges and maintains their sense of autonomy.
Intermediate Familial Alcoholics
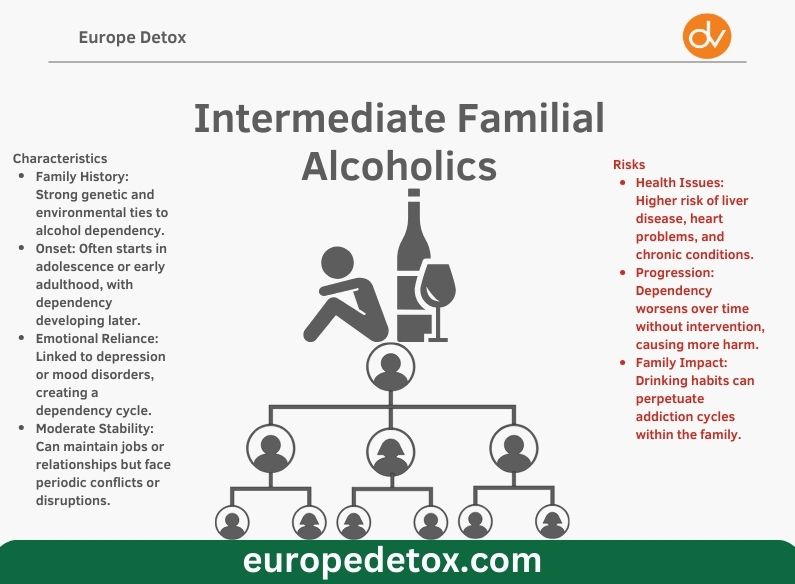
Intermediate familial alcoholics are individuals with a strong family history of alcohol dependency, making up about 18-19% of alcoholics in studies. They often start drinking at an early age and develop dependency in their mid-to-late 30s. Both factors related to environment and genetic background have a significant impact on their drinking behavior.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment for intermediate familial alcoholics often includes addressing both the physical dependency on alcohol and the emotional triggers rooted in family dynamics or mental health. Common approaches include:
Family Counseling: To address underlying issues and repair relationships.
Support Groups: Our clinic offers free consultations with our medical advisors, providing support and guidance for successful recovery.
Therapeutic Interventions: Individual therapy that focuses on coping strategies and breaking generational cycles of addiction.
Starting treatment early is key for this group because it helps with recovery by focusing on mental health and family problems.
Young Antisocial Alcoholics

Young antisocial alcoholics make up about 21% of alcoholics and typically start drinking in their mid-teens, with alcohol dependency developing in their early 20s. This group is characterized not only by heavy drinking patterns but also by coexisting antisocial behaviors or personality traits.
Treatment and Recovery
Young antisocial alcoholics face unique challenges in recovery due to their impulsive nature and possible resistance to authority or structured programs. Treatment often includes:
Behavioral Therapy: Addressing antisocial tendencies and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
Specialized Rehab Programs: Facilities that cater to younger adults and consider the co-occurrence of personality disorders.
Early intervention is critical for this group, as their impulsive behaviors and early dependency place them at higher risk for severe, long-term consequences. With the right support, they can learn to manage their drinking and address the underlying behaviors that contribute to their addiction.
Chronic Severe Alcoholics

Chronic severe alcoholics represent the smallest percentage of alcohol-dependent individuals, accounting for about 9% of cases. This group experiences the most intense and persistent forms of alcohol addiction and is often deeply entrenched in the cycle of dependency.
Treatment and Recovery
Intensive Rehabilitation: This group often requires long-term inpatient rehabilitation programs to manage their addiction and address physical damage.
Medical Detoxification: Given the severity of their dependency, professional medical detox is critical to manage withdrawal symptoms safely.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment: Addressing co-occurring mental health issues alongside alcoholism is vital for effective treatment.
This category of alcoholics faces the hardest challenges in recovery, but with intensive support, consistent therapy, and a structured environment, they can regain control and rebuild their lives.
Global Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) by Demographics
Data for Africa, South America, and Canada were synthesized using global alcohol consumption rates and prevalence studies. Key sources include The World Factbook by the CIA, and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), offering detailed insights into alcohol use disorder (AUD) prevalence and its effects.
Specific estimates for Europe and Asia were derived from regional alcohol consumption statistics and global burden studies. These include data from the Global Health Observatory (WHO) and additional insights from the Alcohol Research: Current Reviews, which explores the social and cultural contexts influencing alcohol use within a social-ecological framework.
Recognizing Alcoholism
Spotting alcoholism isn’t always easy, especially in functional alcoholics who seem to maintain normal lives despite their dependence. If you’re unsure whether you or someone else has a problem, consider these questions:
- Cut: Do you feel the need to cut down on drinking?
- Annoyed: Are you annoyed when people criticize your drinking?
- Guilty: Do you feel guilty about your drinking habits?
- Eye-Opener: Have you ever needed a drink in the morning to steady yourself?
Answering “yes” to two or more of these questions may indicate a drinking problem.
Physical Signs of Alcoholism
Alcoholism can also reveal itself through physical symptoms. If you notice these signs in yourself or someone else, it could indicate a deeper problem:
- Changes in Appearance: Dilated pupils, flushed skin, or noticeable weight changes.
- Frequent Illness: Recurring colds, stomach issues, or fatigue due to a weakened immune system.
- Shaking or Sweating: Symptoms of withdrawal, particularly in the morning or after long periods without drinking.
- Sleep Problems: Insomnia or erratic sleep patterns often linked to alcohol dependency.
We Can Help
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol use, don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re here to support you on your journey to recovery. At our clinic, we understand that individuals seeking treatment for alcohol dependency come from diverse backgrounds and experiences. For instance, approximately 1 in 10 young adults aged 18 to 25 in the United States has an alcohol use disorder.
That’s why we offer free consultations with our medical advisors to help you understand your unique situation and take the first step toward recovery. Our tailored treatment programs address not just the symptoms but also the underlying causes of alcohol dependency, ensuring long-term success and a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Functional alcoholics often underestimate their dependency because they maintain a stable outward life. While some might successfully quit without professional help, most find it challenging due to the hidden psychological and physical dependence. Professional support, including therapy and structured programs, increases the chances of sustained recovery.
Yes, genetics plays a significant role in alcohol dependency. People with a family history of alcoholism (e.g., intermediate familial alcoholics) are at higher risk due to genetic predisposition and environmental exposure.
No. While physical dependence (withdrawal symptoms, tolerance) is common in chronic cases, not all alcoholics experience it. Psychological dependence, where alcohol is used to cope with stress, anxiety, or emotions, can also define alcoholism, particularly in functional and young adult alcoholics.
Some young adult alcoholics reduce or stop drinking as they mature and take on responsibilities. However, continued heavy drinking increases the risk of long-term dependency. Early education, peer counseling, and addressing underlying causes are key to preventing escalation.